Presentation
The neocortex is the center for higher cognitive functions such as language and decision-making. During its embryonic development, neural stem cells known as radial glial (RG) progenitor cells generate all neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes of the neocortex. Two types of RG cells co-exist, with different relative proportions across species. Apical RG (aRG) cells are common to all mammals and localize in the ventricular zone (VZ). They are epithelial cells, anchored to the apical surface through adherens junctions. aRG cells generate neurons indirectly, through the production of an intermediate progenitor, and later on switch to gliogenesis. Basal RG (bRG) cells derive from aRG cells but have delaminated from the neuroepithelium. As such, they are non-epithelial and localize more basally, in the outer sub-ventricular zone (OSVZ). bRG cells undergo a unique form of migration, called mitotic somal translocation (MST), during which their soma very rapidly translocates just before cytokinesis. The abundance of bRG cells varies greatly across species. They are for example very rare in mouse, where they moreover may have limited proliferative properties. They are particularly abundant in certain primates, and especially in humans, where they are believed to account for their massive neocortex size expansion.
Neocortex development. aRG cells are highly elongated stem cells, present both in mouse and human. They contact the brain ventricles apically (down) and the pial surface basally (up). bRG cells are extremely abundant in human but very rare in mouse. They have lost connection to the apical surface and are localized basally. Both aRG and bRG cells can generate the different neuronal subtypes, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Neurogenic divisions can occur through the generation of an intermediate progenitor. |
The neocortex is the center for higher brain functions, such as perception, decision-making and language. Our group focuses on the mechanisms governing neocortex development, with a strong interest on the role and regulation of the neural stem cells.
Cortical development occurs by proliferation of neural stem cells and migration of newborn neurons over substantial distances. In mice, neuroepithelial cells differentiate into apical radial glial cells (aRG), which act as the stem cells of the developing neocortex and give rise to all neocortical neurons, most glial cells and to the adult stem cells. aRG cells are highly elongated, extending a basal process all the way to the pial surface of the developing brain and an apical process that remains in contact with the ventricular surface (Figure. 1). They undergo fascinating cell cycle-dependent nuclear oscillations, a process known as Interkinetic Nuclear Migration (INM). We previously described the mechanism for G2 apical nuclear migration, which involves a Cdk1-triggered recruitment of the dynein motor to the nuclear pore complex (Hu et al., 2013; Baffet et al., 2015). aRG cells can divide asymmetrically to produce one aRG cell and one intermediate progenitor that will divide to produce two neurons.
Although the ventricular zone (VZ), where aRG cells are located, is the major neurogenic region in mice, the situation is very different in humans where 85% of mitoses occur in the sub-ventricular zone (SVZ). As a consequence, this region is massively thicker and becomes subdivided into two morphologically different regions, the inner SVZ (ISVZ) and the outer SVZ (OSVZ). This is largely due to a second type of neural stem cells, called the basal Radial Glial (bRG) cells (also known as oRG cells) (Figure. 1). bRG cells derive from aRG cells and share several characteristics with these cells, such as the extension of a basal process, the expression of a similar set of transcription factors and, most importantly, the capacity to self-renew. bRG cells are very rare in the smooth mouse brain (lissencephalic) and very abundant in the folded human brain (gyrencephalic) and are thought to be fundamental players of the massive size increase of the human brain.
Our group currently focuses on three main topics:
1/ Mechanisms of polarized trafficking in RG cells
In the highly elongated aRG and bRG cells, long-range polarized trafficking occurs to deliver critical molecules, including surface receptors or secreted factors. To investigate these processes, we have recently developed a method for high resolution subcellular live imaging within thick embryonic brain slices. This approach allows to resolve individual fast-moving structures, such as RAB6+ positive vesicles while they are transported in the apical or basal process (Figure 2).
Using this method, we have identified the organization of the microtubule cytoskeleton in RG cells (Coquand et al., 2020).We showed that, while microtubules in the apical process of aRG cells in uniformly oriented basally, microtubules in the basal process display a mixed polarity, reminiscent of the mammalian dendrite (Figure 3). We furthermore showed that this acentrosomal microtubule network is organized from CAMSAP+ varicosities of the basal process, an organization conserved in human bRG cells. We are currently initiating a project aimed at identifying the factors that control this acentrosomal bipolar microtubule network organization.
Our second project aims at identifying the mechanism for post-Golgi apical trafficking in epithelial cells, using aRG cells as a model system (Brault et al, in preparation). Using our live imaging method, as well as a newly generated RAB6A/B double knock-out mouse, we have identified the core machinery that drives post-Golgi transport of the Crumbs apical determinant to the apical surface of mouse aRG cells. We show that impairment of this pathways leads to a delamination of aRG cells that now divide basally, adopting a bRG-like identity. We have now begun a novel project aimed at identifying the mechanisms for basal secretion in RG cells.
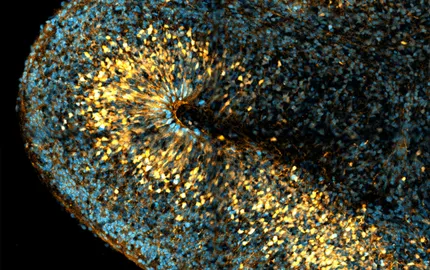
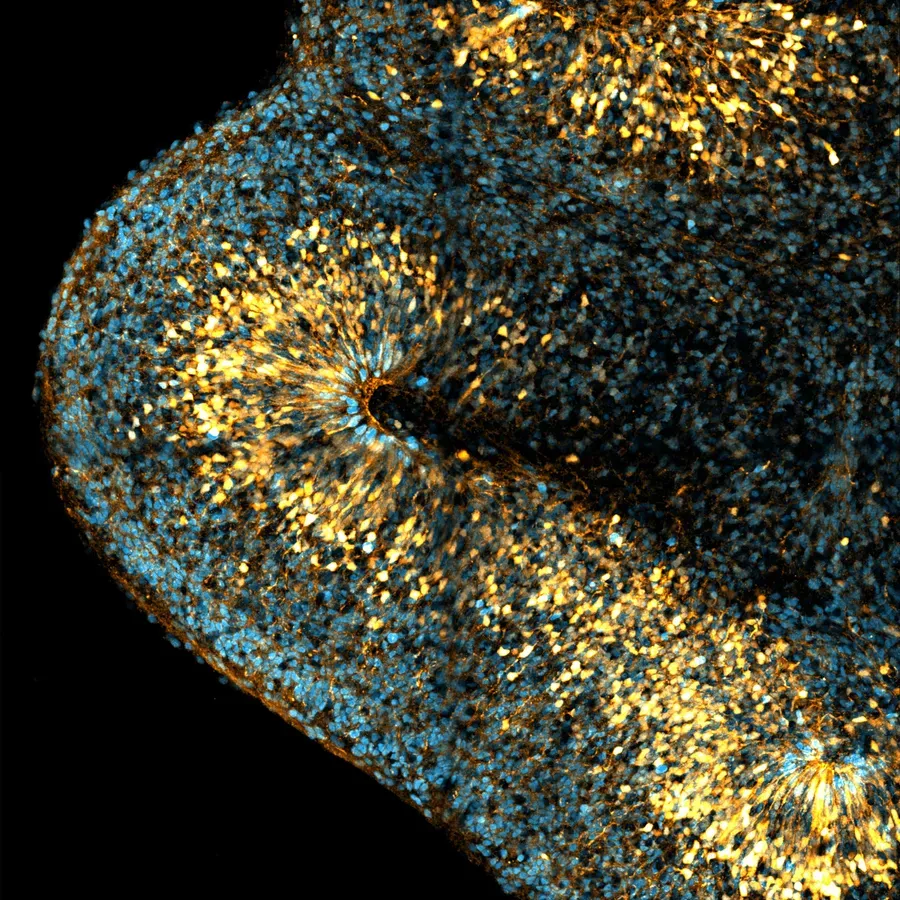
2/ Human neurogenesis
To image human bRG cells, we have established the generation of iPS cell-derived human cerebral organoids. We observe the appearance of bRG cells after 5 weeks of culture, which gradually increases in the following weeks. While organoids usually display mild amounts of bRG cells, our adapted protocol leads to the formation of a large OSVZ containing a very abundant bRG cell population (Figure 4A). In parallel, we have developed the culture and imaging of human fetal brain tissue, obtained through collaborations with two Parisian hospitals (Figure 4B). Because of the dynamic nature of the processes we investigate, we have developed methods for quantitative live imaging of human fetal tissue and cerebral organoids. Tissues are sliced and put into culture for 7 days. Plasmids encoding fluorescent reporters or knockdown constructs are delivered using retroviral infection and slices are live imaged using a CSU-W1 Spinning wide microscope for 24 to 48 hours (Figure 4C, D). Finally, we have developed a protocol to generate in vitro cultures of human RG cells, obtained from human fetal tissue or cerebral organoids. We have developed assays based on microfabrication techniques allowing to align them on micropatterns of adhesion, in order to manipulate their shape (Figure 4E, F).
We currently pursue two main projects that focus on human bRG cells. First, we investigate how fate decisions are made in these cells. We have developed a live-fix correlative microscopy method, that allows us to live image dividing bRG cells in situ, and to identify the fate of the daughter cells. This approach has allowed us to generate a map of bRG cell division modes. Remarkably, this map is highly conserved between human fetal tissue and cerebral organoids (Coquand et al, in preparation). We are now using this knowledge to identify the mechanisms controlling asymmetric cell division, whereby one bRG cells divides into one self-renewing bRG cell and one differentiating cell. In a second project, we are investigating the cytoskeletal-based mechanisms that drive the migration of bRG cells into the developing human neocortex.
3/ Brain Malformations
Alterations in RG cells can lead to a variety of cerebral malformations, which can have genetic or environmental causes (including viral infection). We developed an assay to infect brain slices with flaviviruses and demonstrated that the microcephaly-causing Zika virus (but not other closely-related flaviviruses) specifically infect RG cells and lead to apoptotic cell death (Brault et al., 2016).
In another project, our collaborators have identified mutations in the WDR81 gene that causes extreme microcephaly in newborn children. Using a newly generated WDR81 KO mouse model as well as patient-derived cells, we demonstrated that reduced brain size is specifically due to reduced proliferation rates of RG cells. We showed that WDR81 regulates endosomal trafficking of EGFR, and that loss of function leads to reduced MAP kinase pathway activation (Carpentieri et al., 2020).
Finally, we use patient-derived iPS cells and cerebral organoids to model how mutations can affect human brain development. In particular, we focus on mutations in the DHC1H1 gene, which codes for the dynein heavy chain. Strikingly, our collaborators have identified clusters of mutations that can lead either to cortical malformations, or to motor neuron degeneration (Spinal Muscular Atrophy). We investigate how these different types of mutations differentially affect dynein-based process in the developing cerebral tissue (Farcy et al, in preparation).